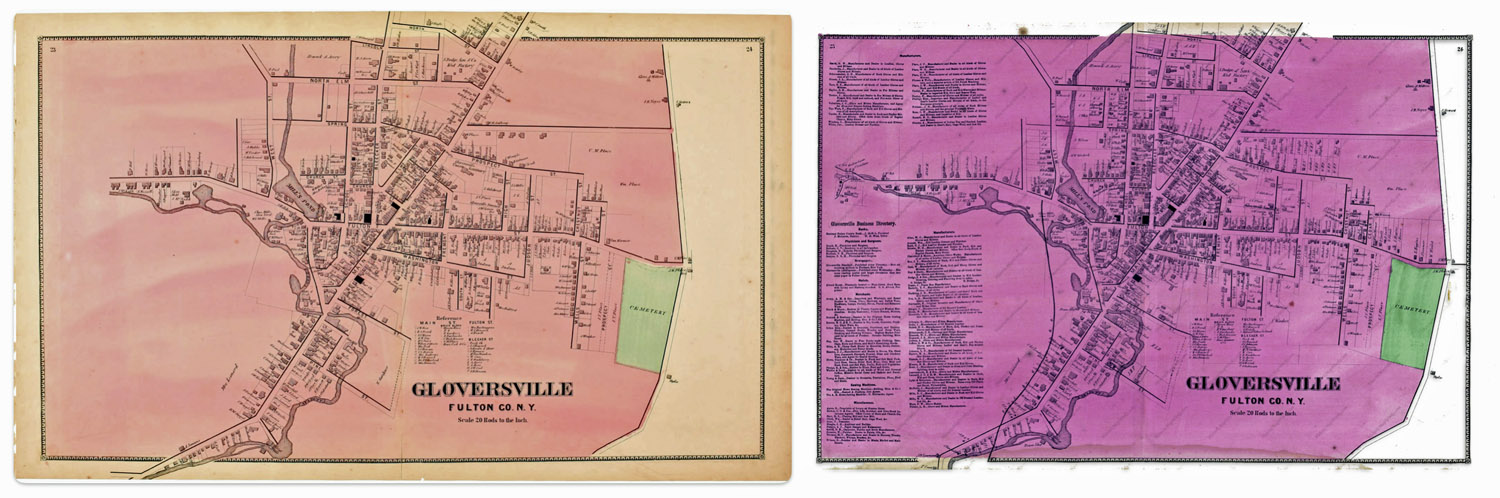
This question on the surface appears to be an arcane question about a specific historical map. What could be the significance of two or more versions of a map? In my research, I have found ‘three’ versions of a map of Gloversville, New York that is found in an Atlas published in 1868. The three versions are largely the same with a few notable differences.
These differences pose questions on whether the information contained in each of the versions of the maps were from different time periods. For example, were the differences the result of purposely leaving certain streets and buildings out of the map? Was the difference of not having a rail line in one map as opposed to another version of the map the results of republishing the atlas with updated information without indicating the publication as a revision?

The Stranahan & Nichols Map of Gloversville in 1868 was part of a local atlas of Fulton and Montgomery counties that also listed businesses on city maps.
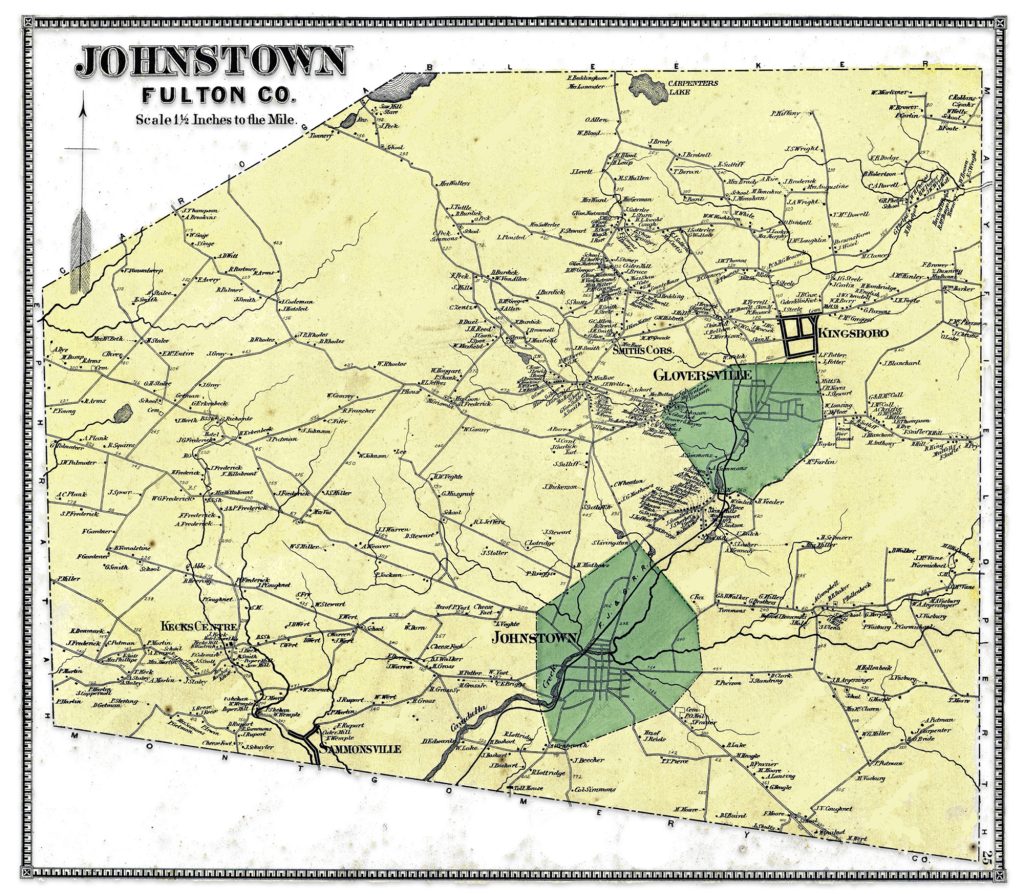
The map in question is part of a larger compendium of maps found in an atlas of Montgomery and Fulton Counties in New York. The atlas was published in 1868. Depending on how long it took to publish the atlas, I figure the information in the maps reflected how the towns and cities in these counties looked like around 1866 or 1867.
The atlas was created by J. Jay Stranahan and Beach Nichols. They were map publishers active in the mid to late 1800s, best known for their atlases of counties in New York state. [1]
In 1868, J. Jay Stranahan and Beach Nichols published the Atlas of Montgomery and Fulton Counties, New York, which contained detailed maps of the two counties and towns in that region including places like Ephratah, Mayfield, Gloversville and Johnstown.
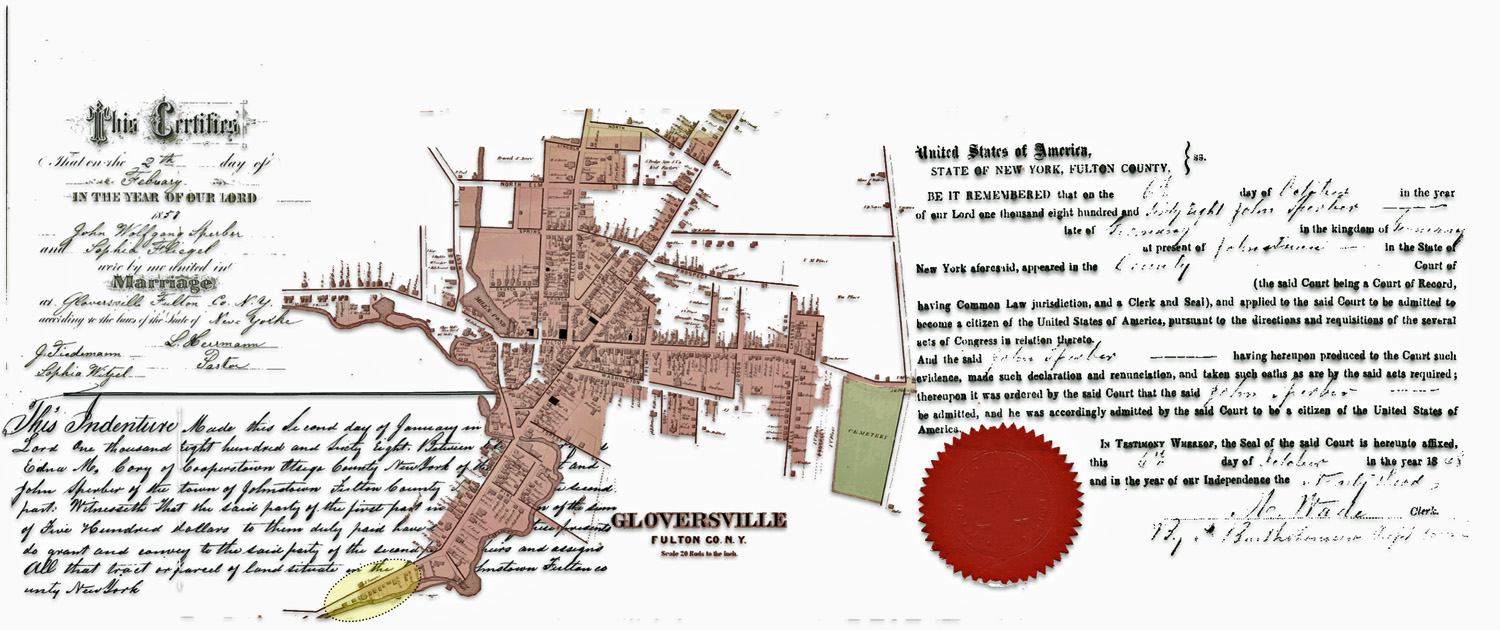
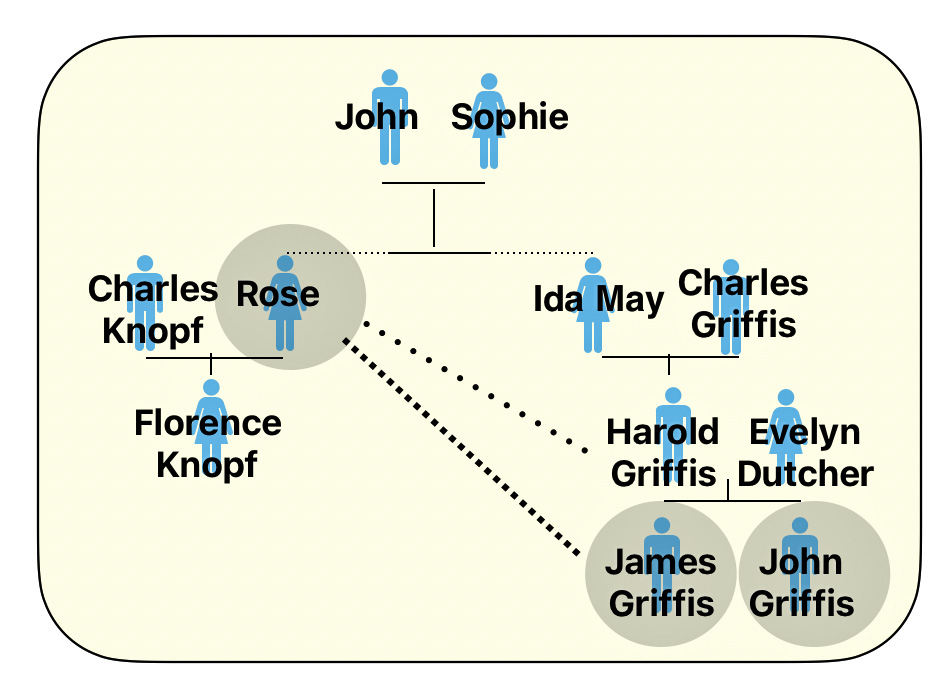
I was interested in this map of Gloversville, New York since it shed light on specific individual relatives and family households that lived in Gloversville at the time that maps were produced.
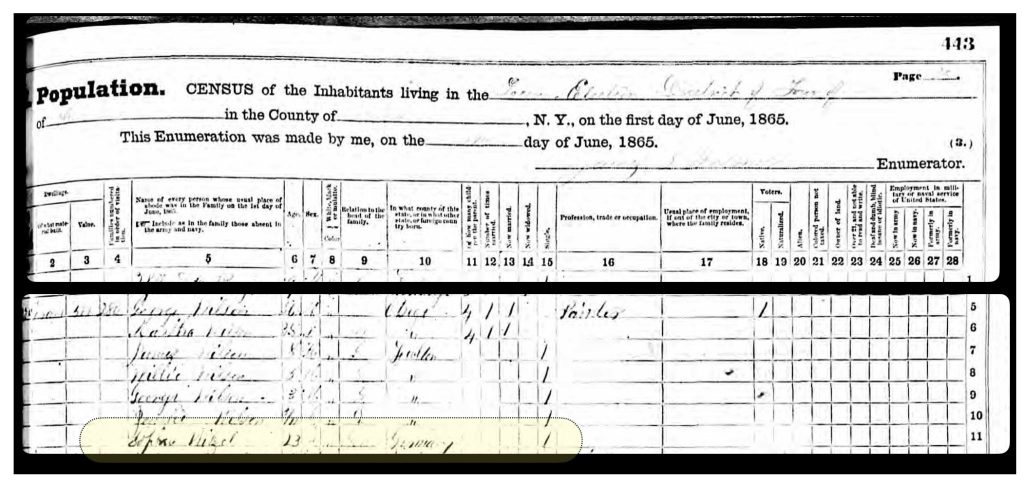
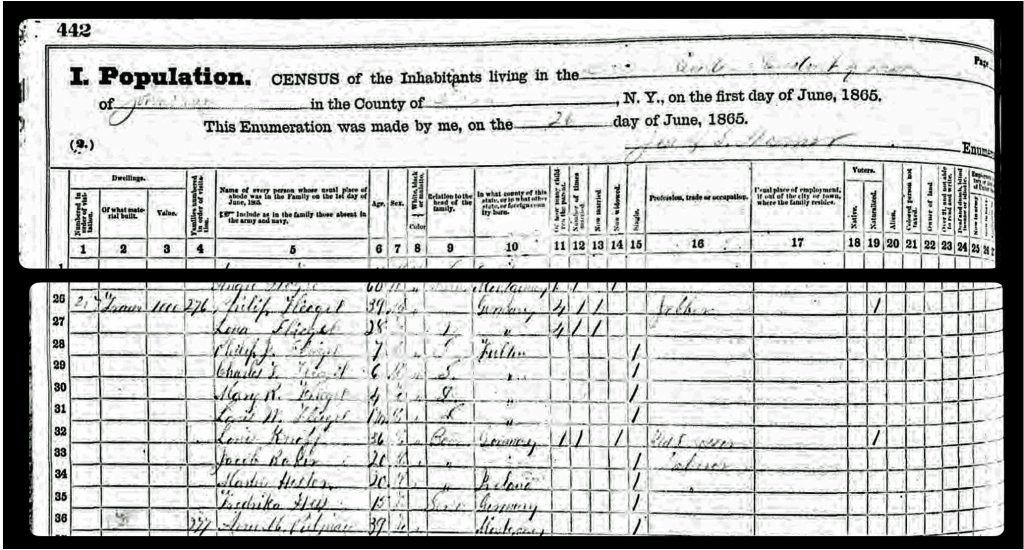
The map had a direct impact on information regarding the location of John Sperber’s house and Louis Knoff’s house and tannery. John Sperber was the maternal grandfather of Harold Griffis. Louis Knoff was John’s brother-in-law.
Stranahan and Nichols Maps in the late 1800s
Beach Nichols led the surveying and map making efforts, with the atlases being created “from actual surveys by and under the direction of B. Nichols”. He was assisted by several people including H.B. Stranahan (likely related to J. Jay Stranahan), W.A. Sherman, H. Loomer, P.A. Cunningham and S.W. Fosdick. J. Jay Stranahan partnered with Beach Nichols to publish the atlases under the company name “J. Jay Stranahan & Beach Nichols”, located at 95 Maiden Lane in New York City. The atlas is 28 leaves in length and contains maps of the two counties.
It appears that J. Jay Stranahan and Beach Nichols produced at least one other historical atlas in addition to the Atlas of Montgomery and Fulton Counties, New York. Stranahan and Nichols also published an Atlas of Herkimer County, New York in 1868.
The fact that they published atlases of three different New York counties in the same year suggests they may have been engaged in a series of New York county atlas projects in the late 1860s.
A distinctive feature of their atlases was their focus on granular detail of these New York counties based on original surveys, rather than covering broader regions. This narrow geographic scope of individual counties appears to set the Stranahan and Nichols atlases apart from many other historical atlases that depict larger areas like full states, countries, continents, or the world.
The maps were drawn from actual surveys conducted by Stranahan and Nichols and their staff. The 1868 atlas featured hand-colored maps showing what specific areas in Fulton and Montgomery counties looked like over 150 years ago. The maps include details of towns, roads, railroads, rivers, and other geographic features. The maps also include the names of individuals who owned various pieces of real estate. This last attribute of the map provides a treasure trove of information for genealogists.
While conducting original surveys was an improvement over just compiling existing maps, survey techniques in the 1800s were not as precise as modern methods. There was likely some inaccuracy introduced in the surveying process. The maps were hand-drafted by Nichols and his assistants based on the survey data. The process of manually transferring survey measurements to the map introduced opportunities for human error and inaccuracy, especially before standardized map symbols were widely adopted.
As was common in the 1800s, features were probably generalized and minor details omitted to avoid overcrowding at the atlas’s scale. This generalization, while necessary, reduces the literal accuracy of the maps. [2]
The maps created by Stranahan and Nichols were part of a broader trend in the late 1800s of map publishers producing detailed county atlases, often based on new surveys, to meet demand for updated, accurate maps as settlement expanded across the country. Their work helped document the geography and development of New York counties during an important period of growth and change in the nineteenth century.
In addition to providing detailed maps of towns and cities, one version of the Stranahan and Nichols map provided brief lists of local businesses surrounding many of the maps in the atlas, similar to information contained in city directories. This version of the atlas was a hybrid of local maps and city directories. Perhaps Stranahan and Nichols saw the utility of fulfilling an unique niche in the map and city directory market by providing maps with the names of business and individuals along with brief lists of businesses on each map.
Large urban centers had city directories by the mid-19th century. Rural communities were sometimes covered in directories by the 1860s. Early city directories focused on businesses and tradesmen. By the mid-1800s, they expanded to include listings of residents, addresses, and occupations. City directories were published annually or biannually by private companies as a resource for salesmen and businesses before the widespread adoption of telephone directories in the early 20th century. [3]
The Three Versions of the 1868 Atlas of Montgomery and Fulton Counties
Table one provides a list of the major sources of the 1868 atlas that I have discovered in my research. Of these sources, all but two contain the same maps. The Internet Archive source only provides a digital copy of the title page. Two of the eight sources contain maps that are different from the other editions that are found in libraries and independent book sellers.
The editions marked in bold in table one are the maps I use in discussing the differences.
Table One: Major Sources of the 1868 Atlas of Montgomery & Fulton Counties
For purposes of discussion, I refer to the original version as the ‘1868 version‘, the second version as ‘1868 revision one‘, and the third version of the map as the ‘1868 revision two’ .
Differences Between the Three ‘1868’ Maps
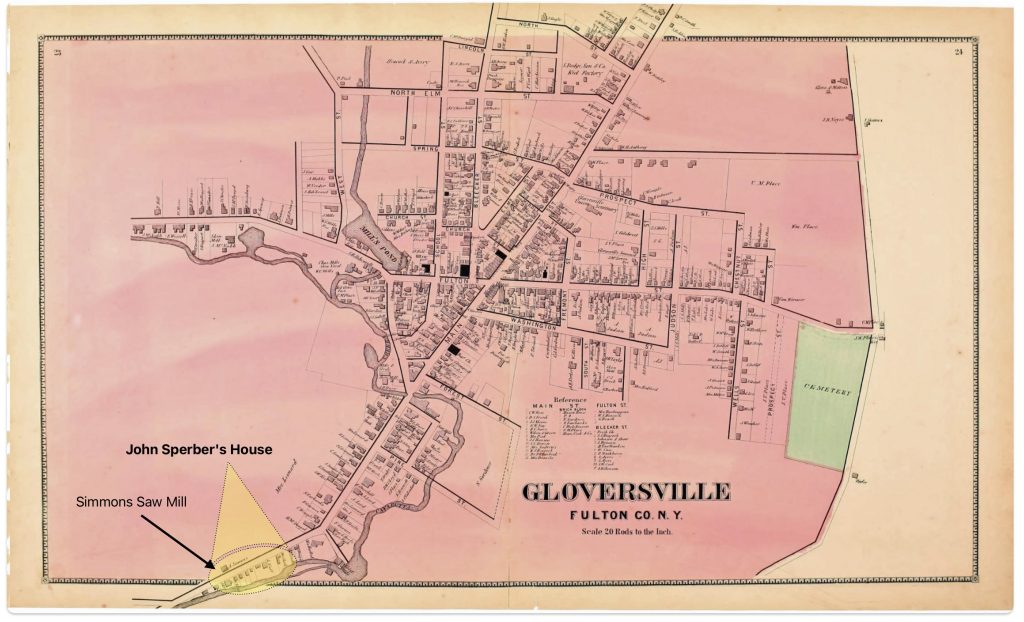
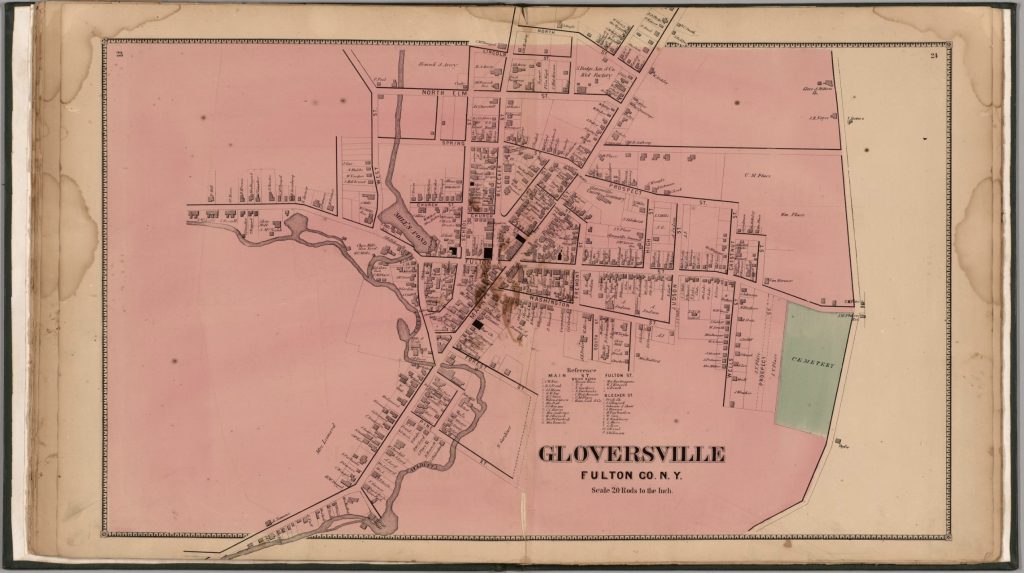
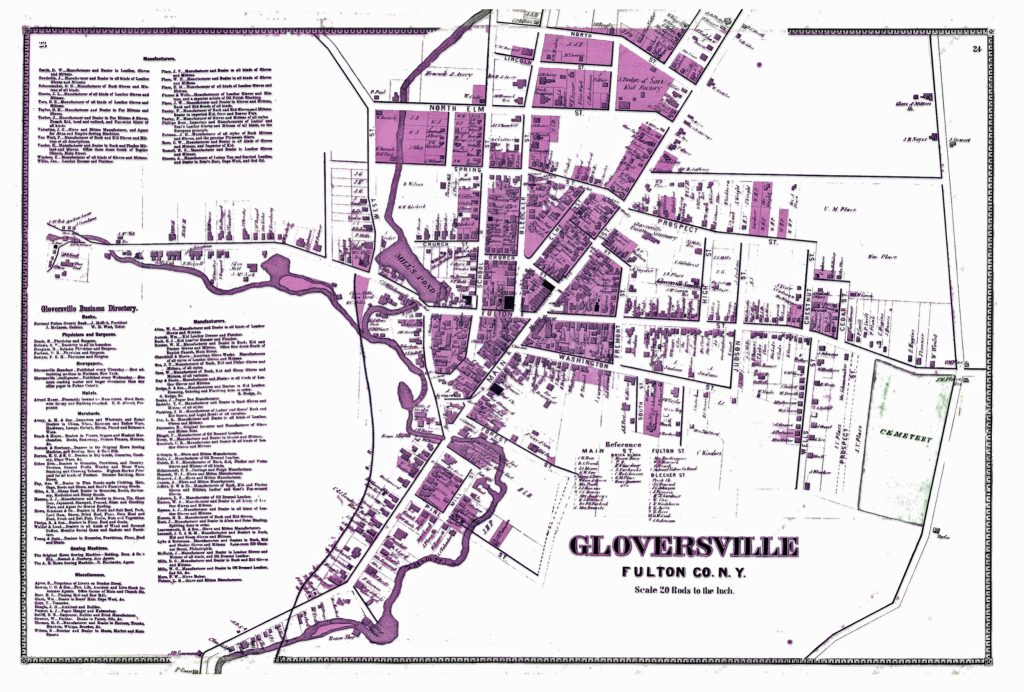
The ‘1868 version‘ of the map is a stylized map of Gloversville in 1868. Not all streets are documented in the map. The map focuses on the major roads in Gloversville. Home owners and owners of businesses are written next to many of the buildings drawn on the streets.
Map One: The 1868 ‘Original Version’ of the Gloversville Map
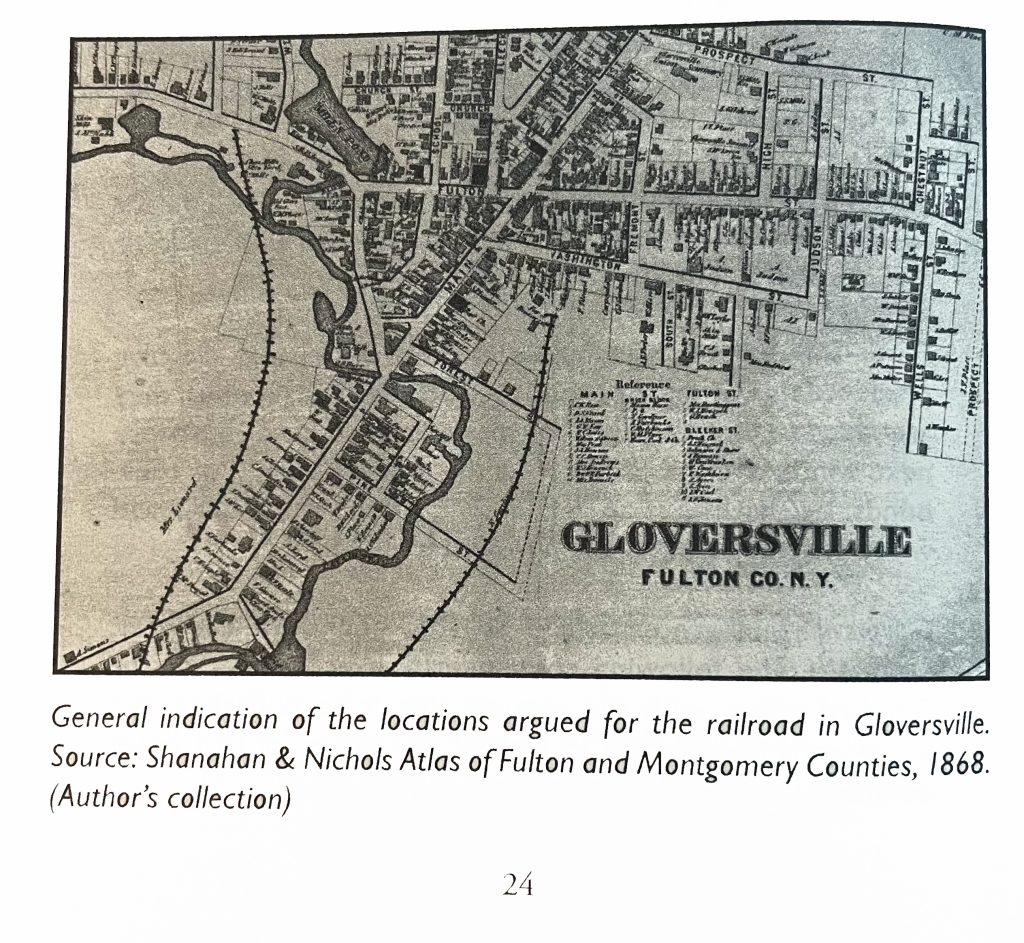
The 1868 ‘map revision one’ is the same as the original map except it has the rail line in the map. This map was found in a book about the Fonda, Johnstown and Gloversville railroad. The author, Paul Larne, claims that the map provides a ‘general path’ of the proposed railroad in the late 1860s.
Map Two: The 1868 ‘revision one ‘ of the Gloversville Map
The 1868 reversion two ‘ map is similar to the first revision map but contains notable differences. There are more street areas documented, a list of manufacturers on the map is provided on the left hand portion of the map, and there is the presence of a rail line.
Map Three: The Revised ‘Version Two’ of the Gloversville Map

Reviewing and comparing the differences between the two versions of the Gloversville map is similar to isolating differences in a ‘Hocus Pocus’ newspaper cartoon. Some of the differences are readily apparent and others are slight.
My review of the two different versions of the ‘1868’ Stranahan & Nichols Gloversville map detect at least eight major differences between the two maps.
These eight differences suggest changes to the original 1868 map were added to a major revision of the map and Atlas after 1868 or there were multiple versions of the atlas published in 1868.
As Larner indicated, the addition of the Fonda, Johnstown & Gloversville Railroad (FJ&G) to the map possibly provided an indication of where the rail line was proposed. Another possibility is the rail line was added after the completion of the rail line.
The FJ&G was incorporated on June 16, 1867 with a capital stock of $300,000. A railroad construction contract was signed on September 18th, 1867.
“By provisions of the contract, the road is to be graded, the track laid, depots and water stations erected, and the whole distance in perfect running order for the cars on or before the first day of September next.” [4]
Progress on the construction of the rail line was slower than anticipated. There were a number of reasons for the delay. The route chosen contained significant obstacles of sand hills, quick sand, and the construction of bridges over cuts of land.
In December of 1867, a local newspaper indicated: “We found a large number of teams and men at work, grading the hill, where the route crosses the Cayadutta, just above the flouring mill. A long trestle bridge, we are informed will span the creek at this point, making the grade gradual and easy. After this grade is overcome, the remainder of the route will be comparatively easy.” [5]
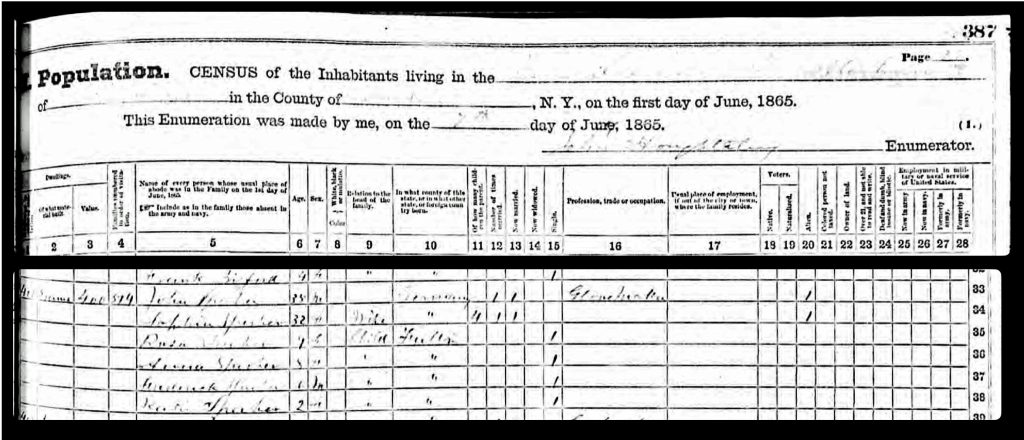
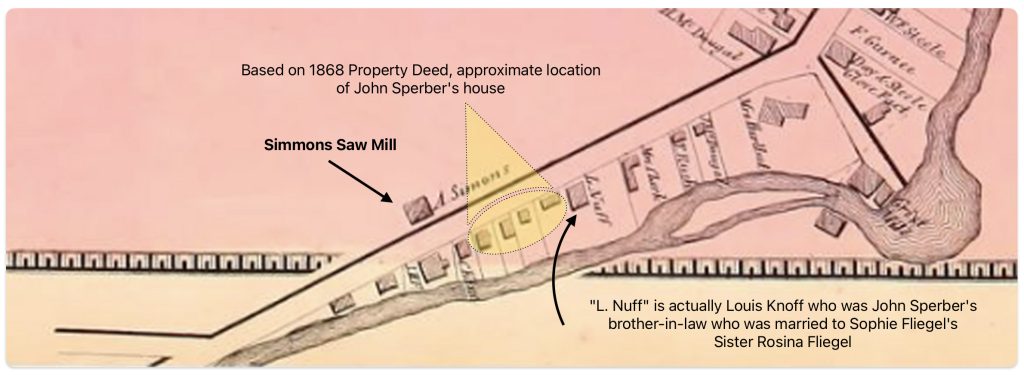
The area where the workers were working over the Cayadutta Creek was where Louis Knoff and John Sperber had property. Knoff purchased his property in 1867 and Sperber purchased his property in 1868. As reflected in map four below, the Knoff property is identified in the ‘1868 version‘ of the map. Evidently, Stranahan and Nichols spelled Knoff’s name phonetically as Nuff.
Map Four: Blow Up Area of the ‘Original 1868 version’ of the Map
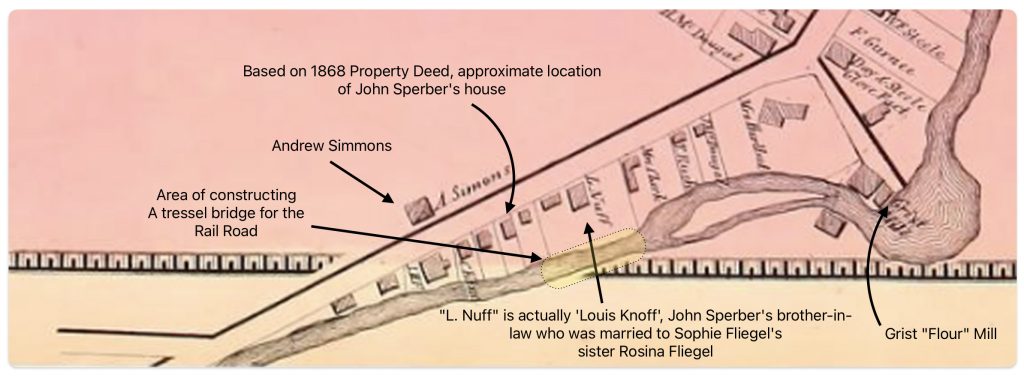
If we look at a blow up of the same area in the ‘1868 reversion two’ map, we see the existence of a rail line going diagonally across Knoff’s property. Knoff’s name is correctly.
Map Five: Blow Up Area of the ‘revised post – 1868 version’ of the Map
It took an additional three years to acquire access to land and build the track from Fonda to Gloversville. The ability to complete this task in three years, given the budgetary demands, the turnover of building contractors, geographical hurdles, court cases and local politics is noteworthy. [6]
On November 29, 1870, the first passenger train pulled by a wood-burning steam engine arrived in Gloversville, marking the completion of the initial 16-mile track section from Fonda to Johnstown and Gloversville. The track was extended another 16 miles from Gloversville to Northville in 1875.[7]
Since the initial FJ&G rail line to Gloversville was not completed until late 1870, the online version of the Atlas provided by Map Works Residential Genealogy was possibly published no earlier than 1871.
An alternative argument is the “1868 reversion one’ map is a modified version of the original map and was published when the rail road that was being built. This version the 1868 map with the rail line is presented in a publication about the creation of the FJ&G railroad. [8]
The major differences between the three versions of the 1868 Atlas are portrayed in the comparison maps below. The Map reversion two is the same as the original version except it has the ‘proposed’ rail line in the map.
Maps Six: Differences between the ‘Original Version’ and ‘Revision Two’ of the ‘1868’ Gloversville Map
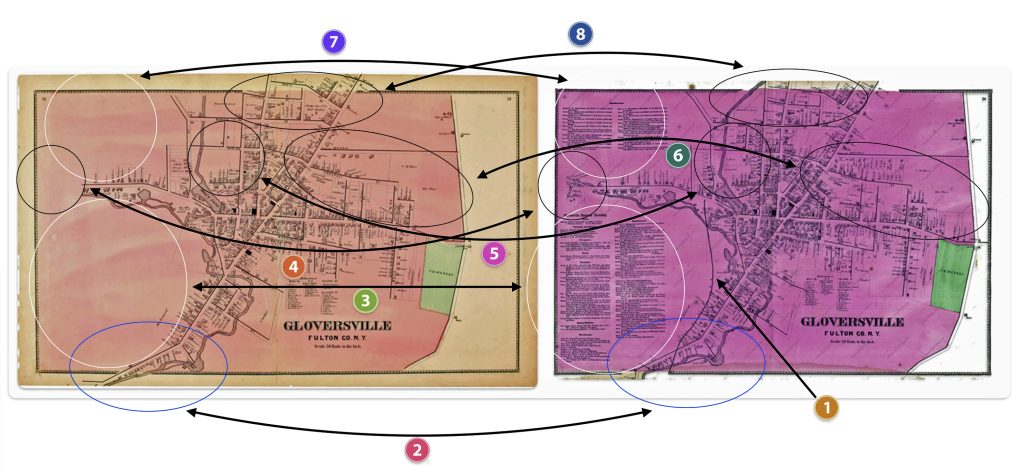
The following are the major differences to the two versions of the Atlas maps of Gloversville.
Table Two: Comparison of the Three Versions of the 1868 Map
| Difference | Rumsey Original Version | Laner Book Revesion one | Map Works Revision Two |
|---|---|---|---|
| One | The FJ&G rail line is absent | The FJ&G rail line is present | The FJ&G rail line is present |
| Two | S. Main Street stops before it curves south | S. Main Street stops before it curves south | S. Main Street continues after it curves south |
| Three | This section is blank | This section is blank | Local manufacturers are listed |
| Four | This section is blank | This section is blank | Map extends road with huses and businesses |
| Five | Map provides major roads in area | Map provides major roads in area | Map provides detailed informaiton on buildings |
| Six | Map provides major roads in area | Map provides major roads in area | Map provides detailed buildings in area |
| Seven | This section is blank | This section is blank | Provides information on local manufacturers |
| Eight | Map provides major roads in area | Map provides major roads in area | Map provides detailed buildings in area |
The ‘Second Revision’ of the 1868 Map
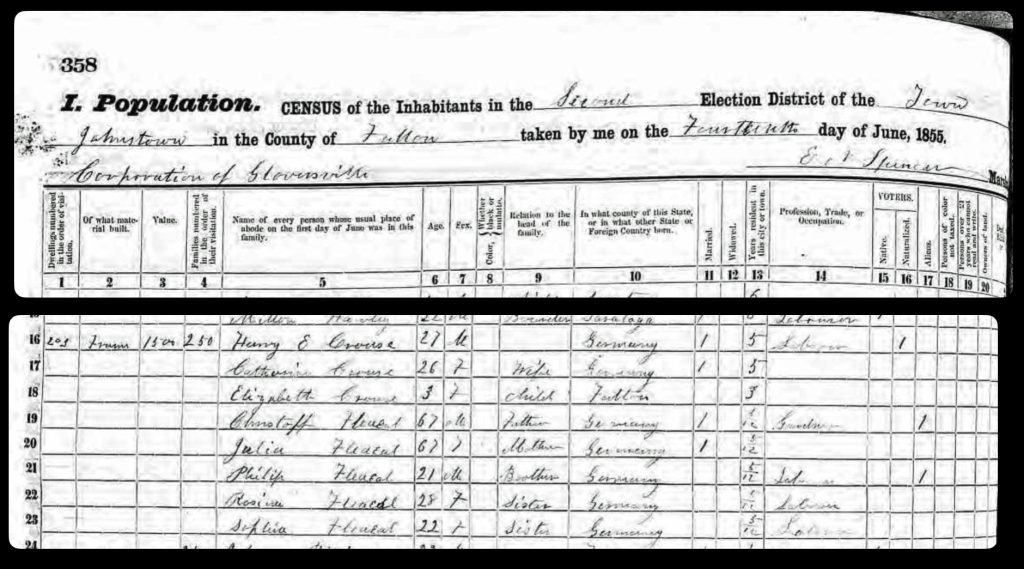
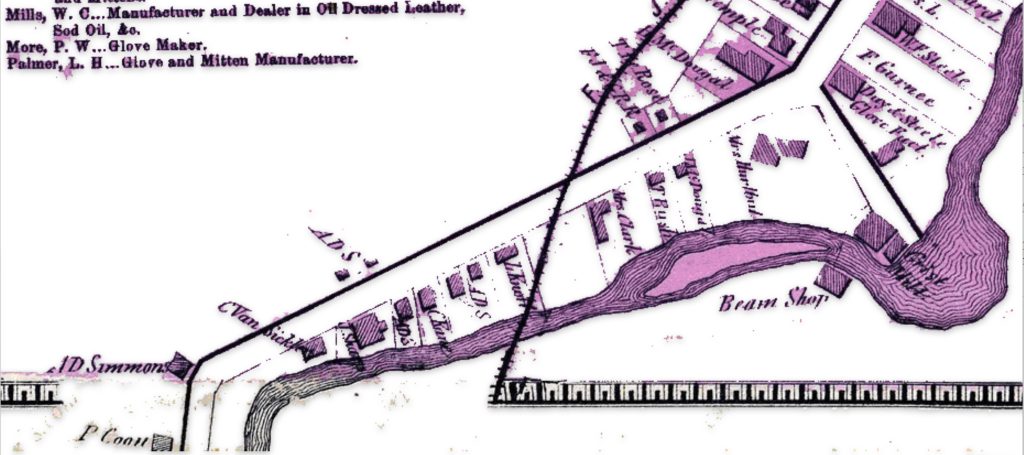
The map is fairly accurate but not exact and does not depict the entire city of Gloversville. The added information in the second revision of the 1886 map has direct import on information on family members in the Griffis family tree. As noted in map seven below, the second revision of the map provides information on Herman Knoff, Philip Fliegel and Henry Krause.
Map Seven: The Nichols Map of Gloversville 1868 – “Map Revision Two” [9]
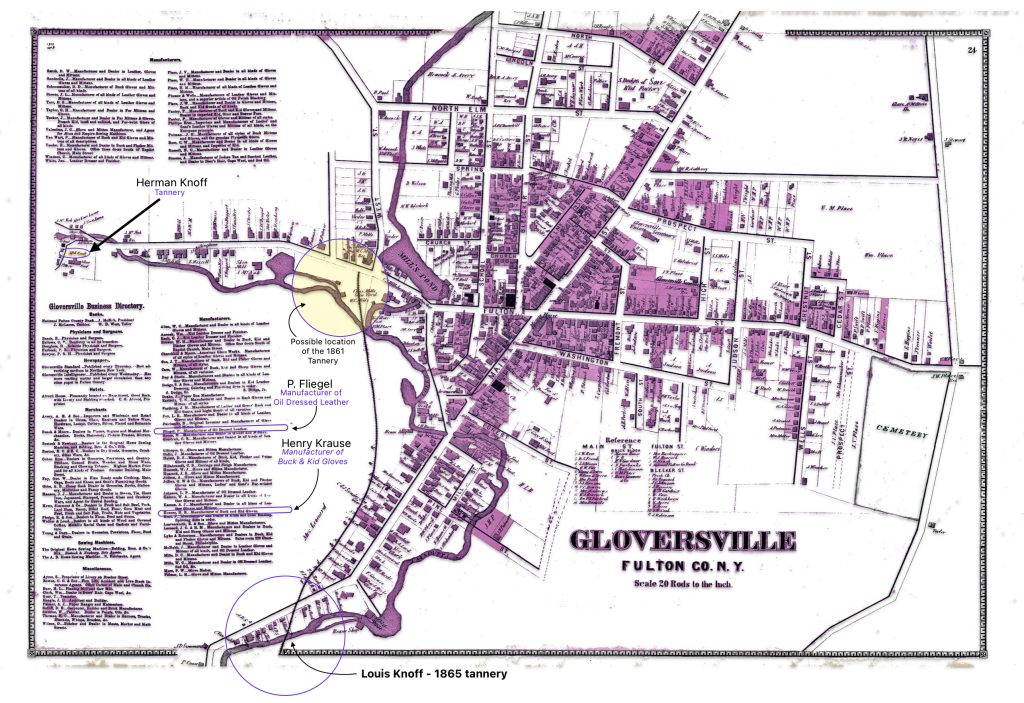
The following map eight is a close up of the location of Louis Knoff’s second tannery that was established, as stated in his obituary, in 1865. [10] It is a blow up of the circled area in map two of the lower left hand portion of the map.
Map Eight: Location of Knoff’s Tannery in 1865
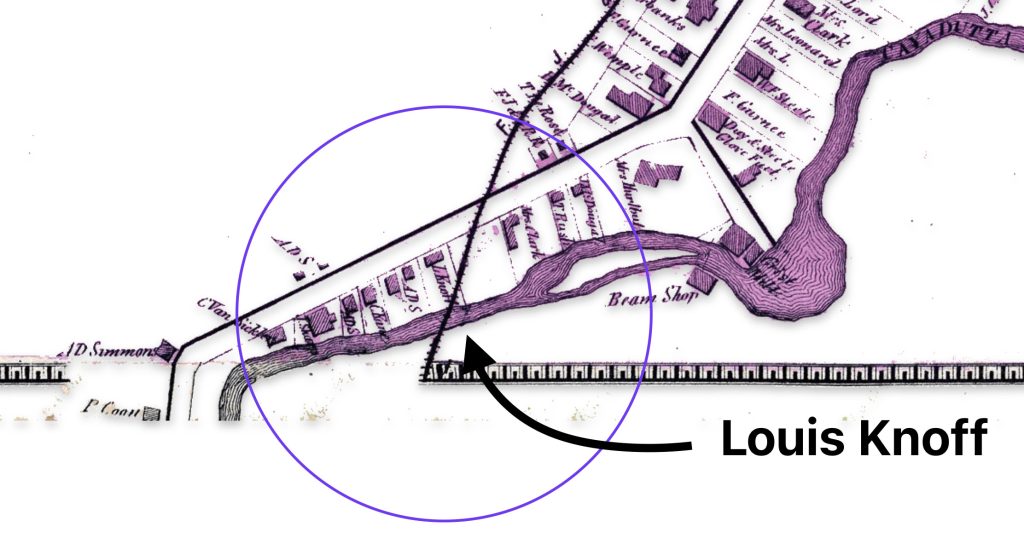
Map nine below is a blow up of a middle portion of the map two which shows where one of Louis’ relatives, Herman Knoff, had a tanning business in 1868. Map nine also shows the possible area where Louis Knoff’s original tannery in 1861 was located. “In 1861 he established his own tanning business and had a tanning mill near the railroad station.” [11]
Map Nine: Location of Knoff’s Tannery in 1861 & Brother Herman’s Tannery in 1868
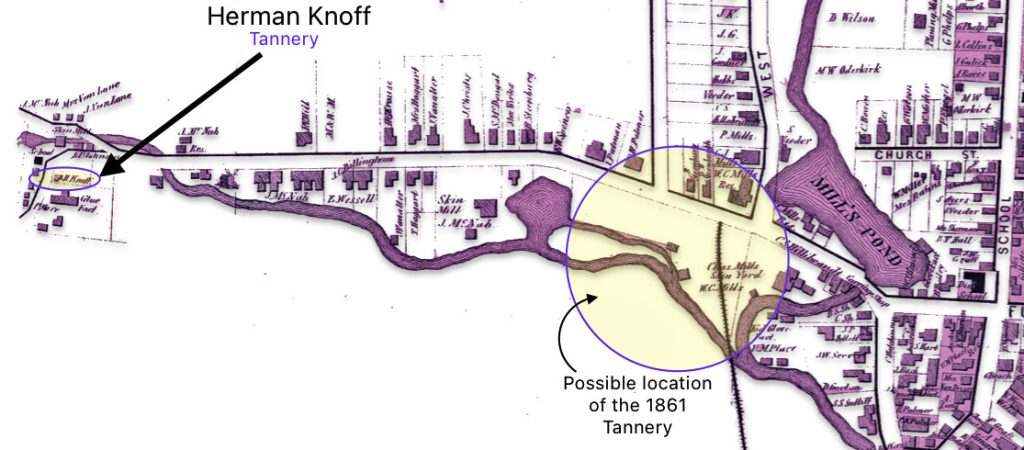
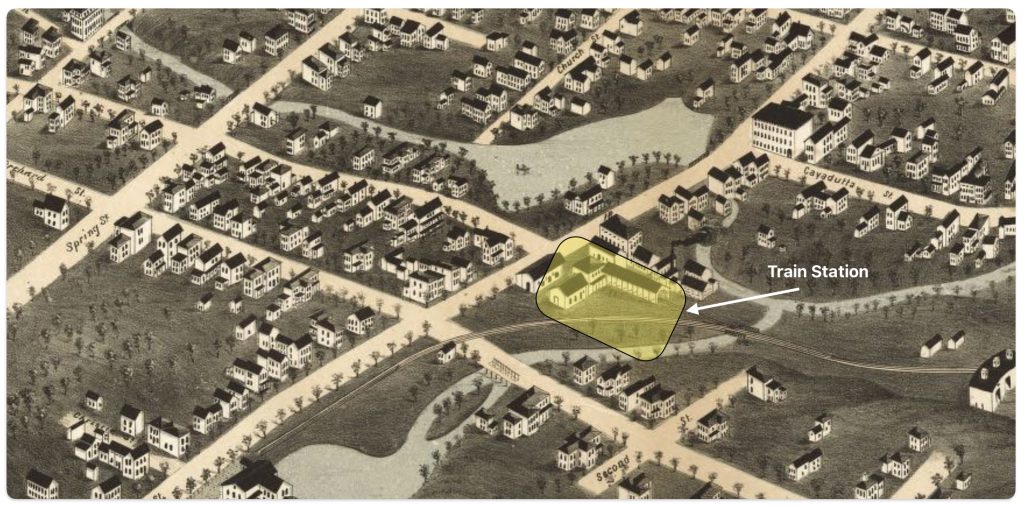
I have indicated in the map above, with a highlighted yellow circle, the approximate location of Louis’ 1861 tannery that was reported to be near where the rail road station existed when his obituary was written. The rail station was not built until 1870 and it obviously is not identified in the 1868 map above. The Gloversville rail station was located on West Fulton Street, close to the site of the present day Rail Station Park. [12]
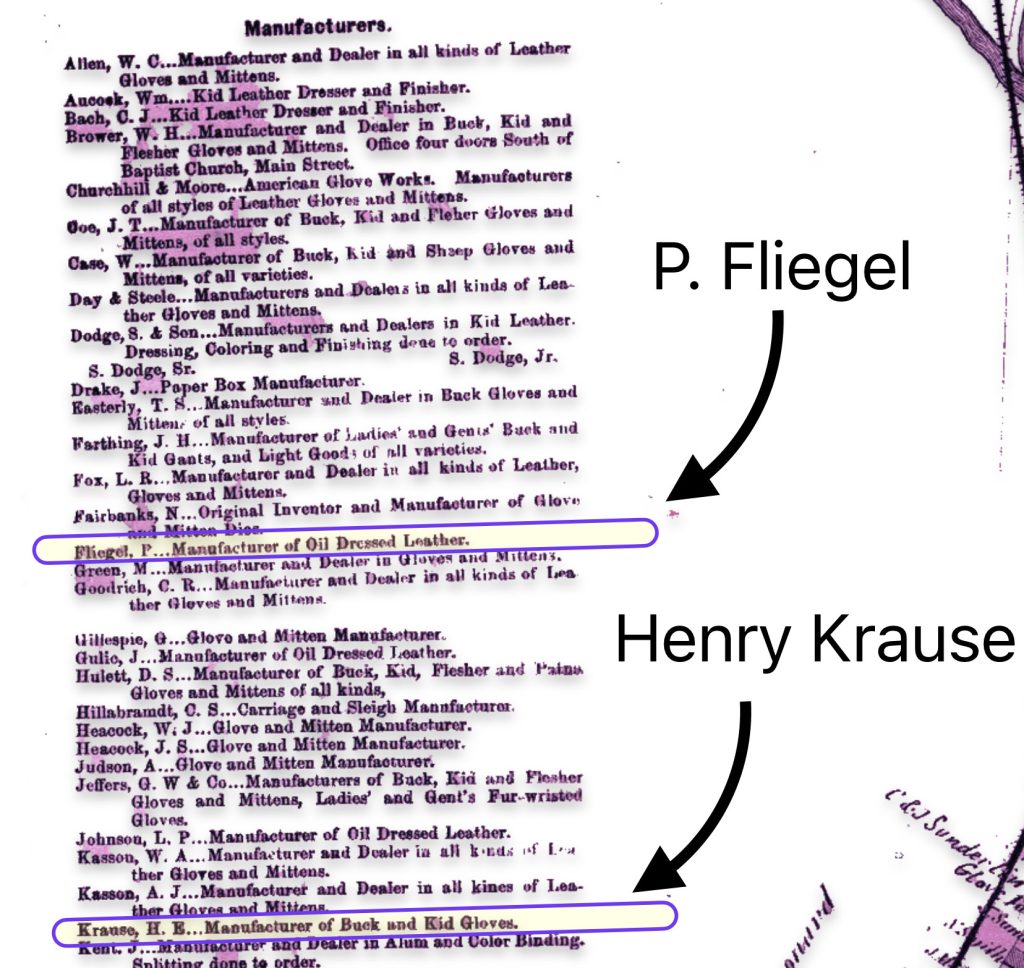
As indicated in map ten, the revised two map also provides a list of local businesses surrounding the map of Gloversville. It is notable that Philip Fliegel and Henry Krause are listed as ‘manufacturers. Philip Fliegel was the brother of Rosa and Sophie. He was listed as a ‘manufacturer of oil dressed Leather’. Henry Krause was the husband of Catherine Fliegel, the sister that first came to America. Henry is listed as a “manufacturer of Buck and Kid Gloves”.
Map Ten: List of Manufacturers as depicted in the Stranahan & Nichols Map of Gloversville in 1868
Conclusion
The Atlas of Montgomery and Fulton Counties, New York provides an authoritative, detailed look at a specific region and time in history. The information contain in the various version of the Atlas maps make it a significant resource for scholars, genealogists, and others researching the history of these New York state counties or life in the post-Civil War. As a primary source, it offers a unique window into the past.
Sources:
Feature Photograph: The banner photo for this page is composed of two of the three versions of the 1868 map of Gloversville: (1) Atlas of Montgomery and Fulton, Published by J. Jay Stranahan and Beach Nichols in 1868, digitalized by the David Rumsey Map Collection, David Rumsey Map Center, Stanford Libraries, https://www.davidrumsey.com/luna/servlet/detail/RUMSEY~8~1~226773~5506920:Gloversville,-Fulton-County,-New-Yo ; (2) Gloversville from Montgomery and Fulton Counties 1868, New York. Published by J. Jay Stranahan and Beach Nichols in 1868, reproduced pages 23 -24 from the original atlas, Historic Map Works Residential Genealogy, https://historicmapworks.com/Map/US/34393/Gloversville/Montgomery+and+Fulton+Counties+1868/New+York/
[1] The Atlas can be found on line and original copies are available for purchase at a number of book store that specialize in historical artifacts and at auction sites.
Nichols, Beach; Loomer, H.; Sherman, W.A.; Cunningham, P.A.; Fosdick, S.W.; Richie, W.W.; Sherwood, E.J.; Guernsey, T.; Vroman, N., Atlas Of Montgomery And Fulton Counties, New York. From actual Surveys by and under the direction of B. Nichols. Assisted by H.B. Stranahan, W.A. Sherman, H. Loomer, P.A. Cunningham And S.W. Fosdick. Published By J. Jay Stranahan & Beach Nichols, 95 Maiden Lane, New York. 1868. Assistants, W.W. Richie, E.J. Sherwood. Assistants, T. Guernsey, N. Vroman. Entered … Stranahan & Nichols in the year 1868 … New York, New York: Stranahan & Nichols, 1868, https://archive.org/details/dr_title-page-atlas-of-montgomery-and-fulton-counties-new-york-from-actual-0668002
Gloversville from Montgomery and Fulton Counties 1868, New York. Published by J. Jay Stranahan and Beach Nichols in 1868, reproduced pages 23 -24 from the original atlas, Historic Map Works Residential Genealogy, https://historicmapworks.com/Map/US/34393/Gloversville/Montgomery+and+Fulton+Counties+1868/New+York/
Atlas of Montgomery and Fulton, Published by J. Jay Stranahan and Beach Nichols in 1868, digitalized by The New York Public Library Digital Collections, https://digitalcollections.nypl.org/items/510d47e3-6ef0-a3d9-e040-e00a18064a99/book?parent=29c2ee00-c5f8-012f-95c2-58d385a7bc34#page/23/mode/2up
Atlas of Montgomery and Fulton, Published by J. Jay Stranahan and Beach Nichols in 1868, digitalized by the David Ramsey Map Collection, David Rumsey Map Center, Stanford Libraries, https://www.davidrumsey.com/luna/servlet/detail/RUMSEY~8~1~226773~5506920:Gloversville,-Fulton-County,-New-Yo
Atlas of Montgomery and Fulton, Published by J. Jay Stranahan and Beach Nichols in 1868, digitalized by FamilySearch, FamilySearch Online Books, https://www.familysearch.org/library/books/records/item/844572-atlas-of-montgomery-and-fulton-counties-new-york
Atlas of Montgomery and Fulton, Published by J. Jay Stranahan and Beach Nichols in 1868 , Dennis Holzman Antiques, original copy available at $350.00 as of August 1 2024, https://holzmanantiques.com/product/atlas-of-montgomery-and-fulton-counties-new-york/
Atlas of Herkimer County, Published by J. Jay Stranahan and Beach Nichols in 1868, Forst Edition leather bound edition available as of August 1, 2024, by AbeBooks seller United Kingdon, Seller Carydale Books, New York, https://www.abebooks.co.uk/first-edition/Atlas-Herkimer-County-New-York-Nichols/22445428577/bd
Atlas of Herkimer County New York published by J. Stranahan & Beach Nichols 1868, copy for sale at $300.00 as of August 1, 2024, Antique Maps of New York, https://www.antiquemapsofnewyorkstate.com/product-page/atlas-of-herkimer-county-new-york-published-by-j-stranahan-beach-nichols-1868
[2] Cartographic generalization, Wikipedia, This page was last edited on 2 June 2024, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cartographic_generalization
Fuechsel, Charles F.. Moderm “Map Making Techniques, Encyclopedia Britannica, 25 Aug. 2024, https://www.britannica.com/science/map/Modern-mapmaking-techniques
History of cartography, Wikipedia, This page was last edited on 22 August 2024, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_cartography
Kain, Roger J. P (ed.). “Cartography in the 19th century”. The History of Cartography. Vol. 5. Chicago and London: University of Chicago Press
[3] Tennant, Melissa, City Directories: More than Basic Facts, 2022, PDF copy: https://griffis.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/City_Directories_handout_2022.pdf , internet location: https://static.libnet.info/frontend-images/pdfs/acpl/Genealogy/City_Directories_handout_2022.pdf
Taylor, Maureen A., The Genealogist’s Guide to Directories, FamilyTree, https://familytreemagazine.com/records/directory/city-directories-genealogy/
Genealogy : Getting Started at The New York Public Library: City directories, Jul 30, 2024, New York Public Library, https://libguides.nypl.org/genealogy/gettingstarted/citydirectories
Weaver, Dan, Book Collecting Guide, Collecting and Using City Directories, Biblio, https://www.biblio.com/book-collecting/what-to-collect/collecting-and-using-city-directories/
Crow, Amy Johnson, What You Might Be Missing in City Directories, Aug 13, 2013, Modern Genealogy Made Easy, https://www.amyjohnsoncrow.com/might-missing-city-directories/
Anonymous, U.S. City Directories, 1821-1989 from Ancestry, 06 03 2015, Evidence Explained: Historical Analysis, Citation & Source Usage, https://www.evidenceexplained.com/content/us-city-directories-1821-1989-ancestry
[4] Gloversville Intelligencer, September 18, 1867, The Railroad Construction Contract Signed.
[5] Johnstown Independent, December 1867
[6] Larner, Paul, Our Railroad: The History of the Fonda, Johnstown & Gloversville railroad (1867 – 1893), Bloomington, Anchor House, 2009, Pages 17 – 44
[7] Burns, Adam, Fonda, Johnstown & Gloversville Railroad, revised March 14, 2024, American-Rails, https://www.american-rails.com/fjg.html
Fonda, Johnstown and Gloversville Railroad, Wikipedia, This page was last edited on 28 December 2022, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fonda,_Johnstown_and_Gloversville_Railroad
Mohawk Valley Democrat, Sept 10, 1870 and the Gloversville Intelligencer, Sept 15, 1870, and Gloversville Intelligencer, Aug 7, 1873. Digital source: https://nyheritage.contentdm.oclc.org/digital/collection/fmcc/id/13/rec/2
[8] Larner, Paul, Our Railroad: The History of the Fonda, Johnstown & Gloversville railroad (1867 – 1893), Bloomington, Anchor House, 2009, Page 24
[9] The original version of this map is found in B Nichols, H.B Stanahan, H. Boomer, P.R. Cunningham and S.W. Fosdick, Atlas of Montgomery and Fulton, New York: J Jay Strachan & Beach Nichols, 1868, https://digitalcollections.nypl.org/items/510d47e3-6ef0-a3d9-e040-e00a18064a99/book?parent=29c2ee00-c5f8-012f-95c2-58d385a7bc34#page/13/mode/2up
The “map reversion two” map in the story is from Historic Map Works: Residential Genealology, Portland, Maine. Historic Map Works has two websites which host historic maps. The first is historicmapworks.com which is aimed at individual subscribers and the second is Historic Map Works Library Edition which supports public libraries and universities.
The majority of their map database was created by scanning an original map at a high resolution and removing major imperfections while maintaining the look of an antiquarian map. The maps are then uploaded and cataloged for viewing on our website. The maps are geocoded each map to a modern map to enable the search by address function. Other methods to view their map collection include browsing by geographic location as well as searching our maps via keywords, town names, makers names, or by year. See: Gloversville, item number #US34393, https://historicmapworks.com/Map/US/34393/Gloversville/
I removed most of the coloring that had been added to the Mapworks version of the Gloversville map. While I purchased a digital copy of the map to respect their reproduction efforts, they have a distracting, reoccurring water mark on the reproduced digital copies of the map. I removed these by removing the colorized layer on the map.
[10] The obituary for Louis Knoff provides a wealth of biographical information on Louis and on his marriage to Rosa Fliegel. The obituary indicates:
- He passed away, primarily due to heart disease, on April 7th, 1893 at 11:30 pm;
- At the time f his death, he lived at 149 South Main Street;
- He was born in Barnstadt, Prussia on January 8, 1828;
- He learned the trade of tanning of leathers in Breslau, Prussia;
- He came to Gloversvlle in 1849 and was employed Gilbert Burr and worked in Johnstown for several years;
- In 1861 he established his own tanning business and had a tanning mill near the railroad station;
- In 1865 he built a factory and tannery on South Main Street;
- He married Pauline Gansel in 1856;
- Pauline died in 1862;
- He remarried Rosa Fliegel in 1866;
- Rosa died in 1891;
- He was survived by two sons Herman and Louis Junior; and
- Louis was a member of the Congregational Curch in Gloversville.
Louis Knoff Obituary, The Gloversville Daily Leader, 8 April 1893, Page 8

[11] Ibid
[12] The Fonda, Johnstown & Gloversville Railroad (FJ&G) was founded in 1867 and construction was completed in 1870, connecting Fonda, Johnstown and Gloversville. The first train ran from Fonda all the way to Gloversville in 1870. When the FJ&G railroad began operations, the Gloversville rail depot would have been located on West Fulton Street where the current Rail Station Park is now situated. The map of Gloversville from 1875 likely shows this original rail station location, just a few years after the railroad opened.
Burns, Adam, Fonda, Johnstown & Gloversville Railroad, revised Mar 14, 2024, American-Rails, https://www.american-rails.com/fjg.html
Ohlhous, Howard C., FJ&G Headquarters, September 20, 2016, The Historical Marker Database, https://www.hmdb.org/m.asp?m=58952
Gloversville Passenger Depot, Front Page Gloversville, http://frontpagegloversville.squarespace.com/pictoral-history/fonda-johnstown-gloversville-railroad/19104344
Fonda, Johnstown and Gloversville Railroad, Wikipedia, This page was last edited on 28 December 2022, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fonda,_Johnstown_and_Gloversville_Railroad
Mohawk Valley Democrat, Sept 10, 1870 and the Gloversville Intelligencer, Sept 15, 1870, and Gloversville Intelligencer, Aug 7, 1873. Digital source: https://nyheritage.contentdm.oclc.org/digital/collection/fmcc/id/13/rec/2